Although the micro molding industry has grown into an intricate and complex field, the concept has been around for much longer than many would think. For over a century, small metal fabricated components have been used in items like wristwatches to facilitate convenience and efficiency in our daily lives. However, the growth of technology and the popularity of increasingly smaller devices such as the iPod and the iPod Nano, have led to an equally increasing demand of micro mold technology.
Some readers may have a basic understanding of what micro molding is from a general standpoint, but a majority won’t be able to answer the question of how micro molding products are made and the technology used to create them. To feed your curiosity for this fascinating and highly popular trade, read on to discover the secrets of micro molding.
How is Micro Molding Made?
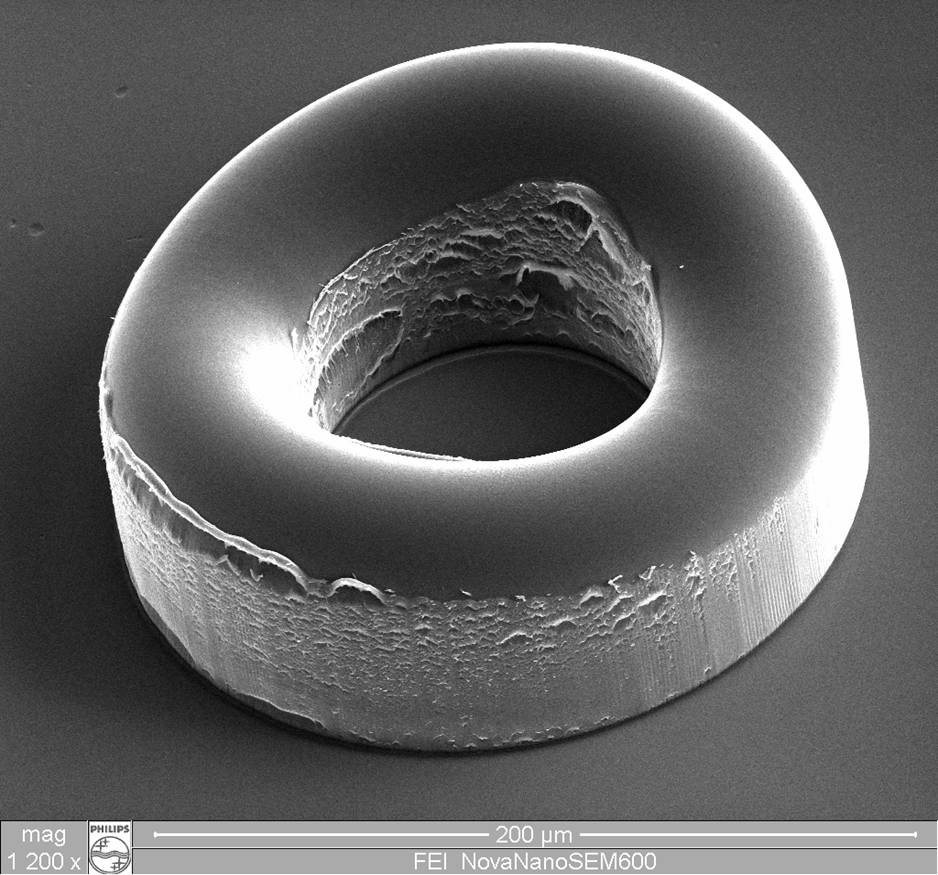
First things first, it should be noted that what most distinguishes micro molding from other aspects of the injection molding industry is not merely the size of the products, but the precision of each part. The challenge of micro molding is to produce large quantities (sometimes in the billions) of small parts with identical precision. That being said, let’s move on to how these parts are made.
The process of creating micro molding often begins with an injection press, many of which are specially designed just for this action. Although these machines account for a significant portion of the work required to produce micro-molding, they are not the only component of the process. High-quality micro molding requires human hands to achieve an ideal final result. This is because micro molding depends on expert tool building, innovation and experience to fit properly in the ultimate destination of each part.
What is Micro Molding Used For?
It’s true that the electronics industry is one of the largest consumers of micro molding products, but these products are just the beginning of the many useful devices that require micro mold technology. In accompaniment with micro-optics, micro molding has led to the development of medical diagnostics, endoscopic tools, minimally-invasive surgical tools and micro-sensor applications. In addition to micro molding’s contribution to the medical field, it has also benefited the telecommunications and automotive market sectors. This process has further been used in many miscellaneous devices such as hearing aids, switches, sensors, lenses, catheters, rollers, fiber-optic components and more.
Essentially any advanced, high-tech tool that requires impeccable precision in a tiny form has utilized micro molding in some form. If you compare the sizes of modern technological tools with their parent counterparts, it’s easy to see how micro molding has developed to accommodate these smaller devices. For example, look at a basic cell phone from the 1990s compared to the average smartphone today. Micro molding is not only facilitating smaller, more convenient devices, but is actually improving the multi-functionality of these devices as well.
It’s easy to dismiss or underappreciate the extreme levels of precision and technology that went into making devices we use every day. However, knowing a little more what the process entails can ensure a better understanding of this booming industry and how it has enriched all of our lives for the better.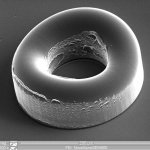





















Leave a Reply